Quick Start Guide
Get started with Easy Email Pro in minutes. This guide will walk you through the basic setup and implementation of the email editor.
Option 1: Use Demo Templates
The quickest way to get started is to use our pre-built demo templates. Browse our collection of starter templates at our GitHub repositories.
Option 2: Manual Setup
If you prefer to set up from scratch, install the required packages:
Step 1: Install Dependencies
pnpm install easy-email-pro-core easy-email-pro-editor easy-email-pro-theme easy-email-pro-kit @arco-design/web-react @arco-themes/react-easy-email-pro mjml-browser slate slate-react slate-history
Or with npm/yarn:
npm install easy-email-pro-core easy-email-pro-editor easy-email-pro-theme easy-email-pro-kit @arco-design/web-react @arco-themes/react-easy-email-pro mjml-browser slate slate-react slate-history
Follow these steps to create your first email editor:
Step 2: Create Your Editor Component
First, install all required packages using your preferred package manager:
import React, { useMemo, useRef } from "react";
import { EmailEditorProvider, EmailTemplate } from "easy-email-pro-editor";
import {
EditorContextProps,
Retro,
ThemeConfigProps,
} from "easy-email-pro-theme";
import "easy-email-pro-theme/lib/style.css";
import mjml from "mjml-browser";
// Theme style, If you need to change the theme, you can make a duplicate in https://arco.design/themes/design/6979/setting/base/Color
import "@arco-themes/react-easy-email-pro/css/arco.css";
import templateData from "./template.json";
import { EditorCore } from "easy-email-pro-core";
import axios from "axios";
export default function MyEditor() {
const instanceRef = useRef<EditorContextProps | null>(null);
// Initialize editor with template data
// You can fetch this data from your server or use a local JSON file
const initialValues: EmailTemplate = useMemo(() => {
return {
subject: templateData.subject,
content: templateData.content,
};
}, []);
// Handle file uploads (images, etc.)
// Replace this with your actual upload implementation
const onUpload = async (file: Blob): Promise<string> => {
// Example: Upload to your server or CDN
// const formData = new FormData();
// formData.append("file", file);
// const response = await fetch("/api/upload", {
// method: "POST",
// body: formData,
// });
// const { url } = await response.json();
// return url;
// For demo purposes, return a placeholder URL
return Promise.resolve(
"https://res.cloudinary.com/dfite2e16/image/upload/v1681907056/clgnivsuj0018z9ltiixmxf6k/ilh6rri61f512i7wb6yd.png"
);
};
// Handle form submission
// This is called when the user clicks the save/submit button
const onSubmit: ThemeConfigProps["onSubmit"] = async (values, editor) => {
console.log("Template values:", values);
console.log("Editor instance:", editor);
// Convert the template to MJML format
const mjmlStr = EditorCore.toMJML({
element: values.content,
mode: "production",
beautify: true,
});
// Convert MJML to HTML using mjml-browser
const html = mjml(mjmlStr).html;
// Send to your backend API
await axios.post("/your-server-url", {
content: values.content,
subject: values.subject,
html: html,
});
};
// Handle real-time changes
// This is called whenever the template is modified
const onChange: ThemeConfigProps["onChange"] = async (values, editor) => {
console.log("Template changed:", values);
// Optional: Auto-save, validation, etc.
};
// Configure the editor with all necessary options
const config = Retro.useCreateConfig({
// Client ID for paid plans (optional for free tier)
// After subscribing to a paid plan, you'll receive a client ID from support
clientId: process.env.CLIENT_ID,
// Reference to access editor instance programmatically
instanceRef: instanceRef,
// Editor height
height: "calc(100vh - 66px)",
// Required handlers
onUpload,
initialValues: initialValues,
onSubmit: onSubmit,
onChange: onChange,
// UI Features
showSourceCode: true, // Show JSON source code panel
showLayer: true, // Show layer tree in sidebar
showPreview: true, // Show email preview
showSidebar: true, // Show left sidebar with blocks
showBlockPaths: true, // Show breadcrumb path for selected block
compact: false, // Single or double sidebar layout
showDragMoveIcon: true, // Show drag handle icons
showInsertTips: true, // Show insertion hints
// Feature Flags
enabledAutoComplete: true, // Enable automatic container structure completion
});
return (
<EmailEditorProvider {...config}>
<Retro.Layout></Retro.Layout>
</EmailEditorProvider>
);
}
template.json
{
"subject": "Welcome to Easy Email Pro",
"content": {
"data": {
"breakpoint": "480px",
"globalAttributes": {
"font-family": "Arial, sans-serif"
}
},
"type": "page",
"children": [
{
"type": "standard-section",
"data": {},
"attributes": {},
"children": [
{
"type": "standard-column",
"data": {},
"attributes": {},
"children": [
{
"type": "placeholder",
"data": {},
"attributes": {},
"children": [
{
"text": ""
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
],
"attributes": {
"background-color": "#f5f5f5",
"content-background-color": "#ffffff"
}
}
}
Step 3: Template Structure
The template follows a hierarchical structure. Here's a minimal template structure:
template.json
{
"subject": "Welcome to Easy Email Pro",
"content": {
"data": {
"breakpoint": "480px",
"globalAttributes": {
"font-family": "Arial, sans-serif"
}
},
"type": "page",
"children": [
{
"type": "standard-section",
"data": {},
"attributes": {},
"children": [
{
"type": "standard-column",
"data": {},
"attributes": {},
"children": [
{
"type": "placeholder",
"data": {},
"attributes": {},
"children": [{ "text": "" }]
}
]
}
]
}
],
"attributes": {
"background-color": "#f5f5f5",
"content-background-color": "#ffffff"
}
}
}
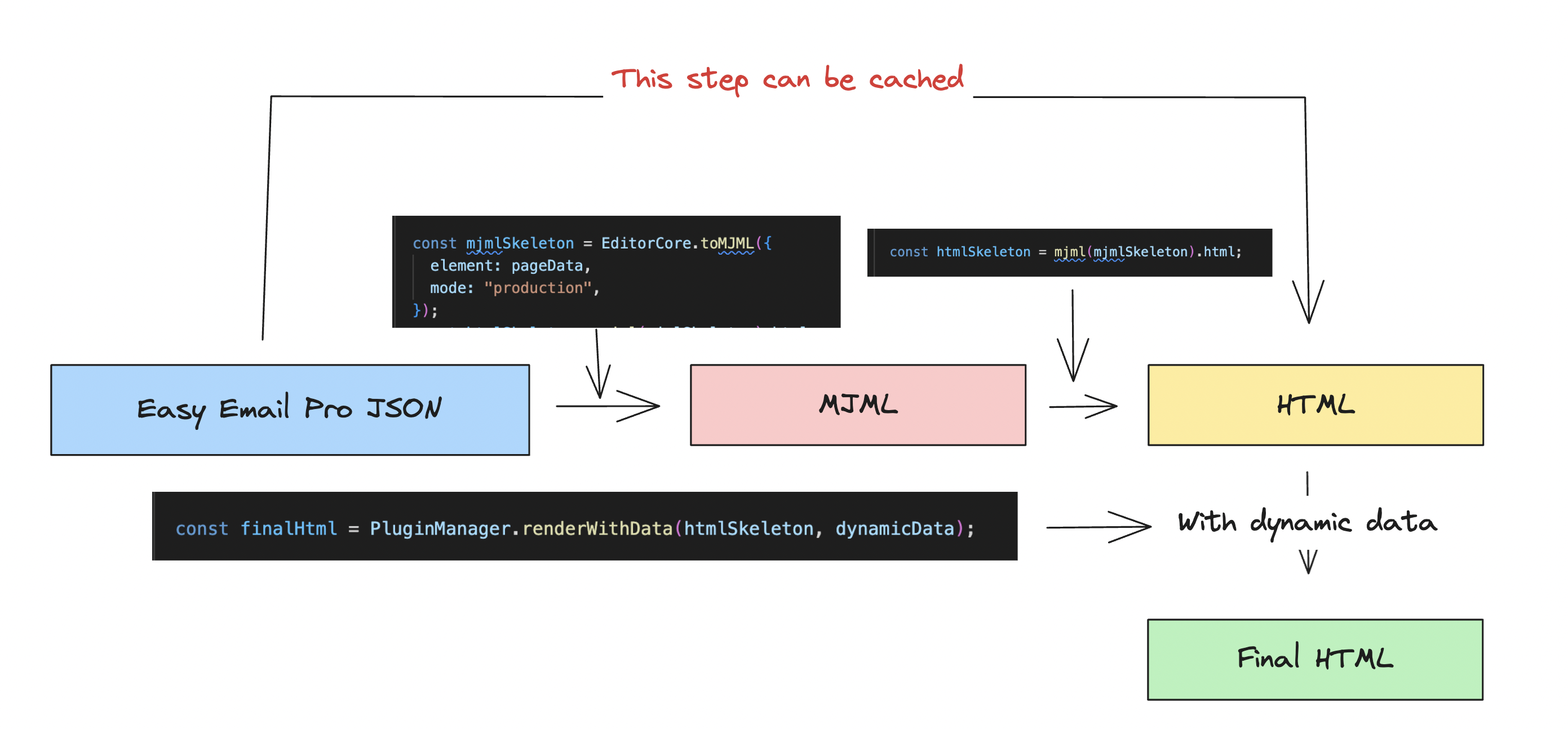
How It Works
Easy Email Pro uses a two-stage rendering process:
- Edit Mode: Uses React components for interactive editing
- Production Mode: Converts to MJML, then to HTML for email clients
Next Steps
Now that you have a basic editor set up, explore these resources:
- Live Demo: Try the full-featured editor at https://demo.easyemail.pro
- Demo Code: Check out complete examples at https://github.com/easy-Email-Pro/
- Configuration: Learn about all configuration options in the Configuration Guide
- Examples: Browse practical examples in the Examples Section
- API Reference: Dive into the API Documentation
Common Next Steps
- Customize Block Categories: Configure which blocks appear in the sidebar
- Add Custom Blocks: Create your own reusable components
- Integrate with Backend: Connect file uploads and template saving to your API
- Customize Theme: Match the editor's appearance to your brand
- Add Localization: Support multiple languages